Although 45% of small businesses do some form of online advertising, pay-per-click is still a concept that eludes many of us.
As a marketer, PPC is a skill that you should have in your tool belt — or at least have a basic understanding of.
This guide will help you grasp pay-per-click marketing in its entirety. To start, we’ll begin with the benefits of paid advertising and then get into some key definitions that you’ll need to know.
What is PPC?
Pay-per-click, or PPC, is a form of advertising that allows you to pay a fee to have your website on the search engine result page (SERP) when someone types in specific keywords or phrases to the search engine. The SERP will display the ads you create to direct visitors to your site, and the fee you pay is based on whether people click your ad.
When done right, PPC can earn you quality leads. If you can create a seamless user journey (which you’ll learn how to do later in this piece), it could mean a massive ROI for your PPC efforts.
Pay-per-click advertising is most common in search engine results pages, like Google or Bing, but is also used on social channels (although CPM is more common).
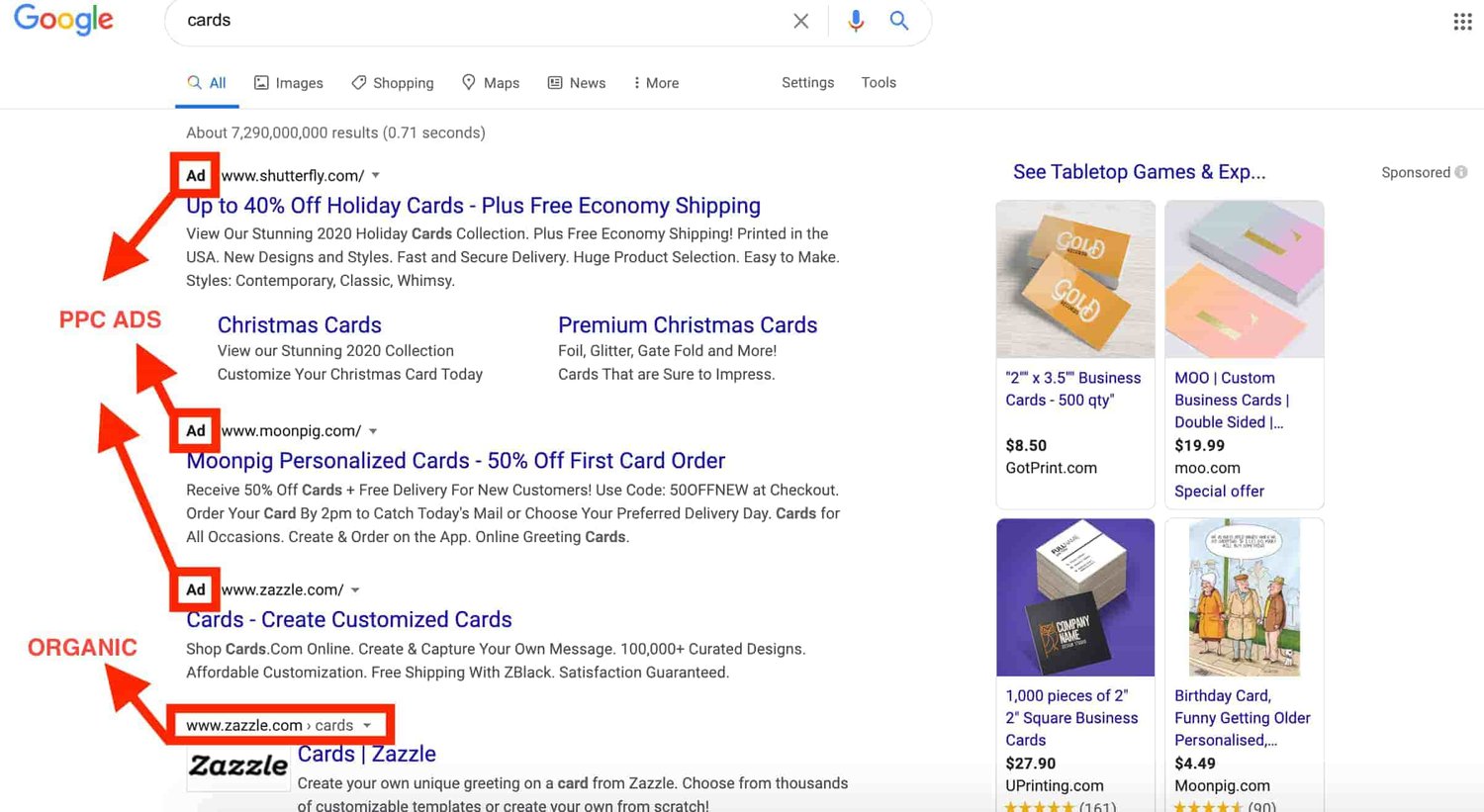
If you’re wondering where you can find pay-per-click ads, they’re the results you see before and to the right of the organic search results. For instance, check out the ad that came up in my search for "cards.”
PPC Terms and Definitions
What’s a marketing channel without a few acronyms and a little jargon?
If you’re going to enter the paid advertising space, there are a few terms you should know. Below, we review the main elements of a PPC campaign, ranging from broad to the more specific.
Search Engine Marketing (SEM)
The objective of all forms of digital advertising is to rank for a target keyword, which you can do in several ways. Search Engine Marketing (SEM) refers to any digital marketing (paid or unpaid) done on a search engine, like Google, Yahoo, or Bing.
SEM is an umbrella term that encompasses both paid advertising and search engine optimization, that is, ranking organically for keywords. It’s important to note that not all PPC occurs on search engines — social media has PPC ads, too (think: Facebook Ads).
CPC
Cost-per-click (CPC) is the amount that an advertiser pays for each click on your ad. CPC acts as your bid in an auction that determines where your ad will be placed. As you can imagine, a higher bid equates to better ad placement.
You set your CPC at the maximum price you are willing to pay per click on your ad. What you actually pay is determined by the following formula:
(Competitor’s Ad Rank / Your Quality Score) + 0.01 = Actual CPC.
Let’s go over the terms in this equation, so you know what you’re paying for:
Ad Rank
This value determines the position of an ad on a search engine results page. It’s equal to Maximum Bid x Quality Score.
Quality Score
This is the score that search engines give to your ad based on your clickthrough rate (CTR) — measured against the average CTR of ads in that position — the relevance of your keywords, the quality of your landing page, and your past performance on the SERP.
Maximum Bid
This is the maximum you're willing to pay per click on your ad.
Here’s an image by WordStream that illustrates what I mean:
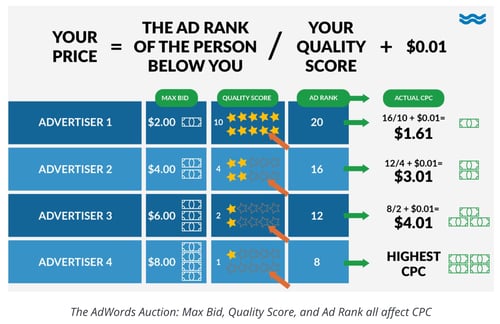
You can set your CPC to manual, where you determine the maximum bid for your ads, or enhanced, which allows the search engines to adjust your bid based on your goals. One of these enhanced options involves bid strategies that automatically adjust your bids based on either clicks or conversions.
CPM (Cost per Mille)
CPM, also known as cost per thousand, is the cost per one thousand impressions. It’s most commonly used for paid social and display ads. There are other types of cost-pers… like cost-per-engagement, cost-per-acquisition (CPA), but for the sake of preserving your mental space, we’re going to stick with clicks, a.k.a. CPC.
Campaign
The first step in setting up your PPC ads is determining your ad campaign. You can think of your campaign as the key message or theme you want to get across with your advertisements.
Ad Group
One size doesn’t fit all. That’s why you’ll create a series of ads within your campaign based on a set of highly related keywords. You can set a CPC for each ad group that you create.
Keywords
Each ad within your ad group will target a set of relevant keywords or key terms. These keywords tell search engines which terms or search queries you want your ad to be displayed alongside in SERPs. Once you determine which keywords perform best, you can set a micro CPC specifically for keywords within your ads.
Ad Text
Your keywords should inform your ad text. Remember, your Quality Score is determined by how relevant your ad is; therefore, the text in your ad (and landing page, for that matter) should match the keyword terms you’re targeting.
Landing Page
A landing page is a critical piece of your paid advertising strategy. The landing page is where users will end up once they click your PPC ad. Whether it’s a dedicated webpage, your homepage, or somewhere else, make sure to follow landing page best practices to maximize conversions.
Best PPC Platforms
Now that you understand the PPC basics, I’m guessing your next question is: Where should I advertise?
There are dozens of online spaces where you can spend your coveted ad money, and the best way to vet them is by taking a close look at your potential ROI on each platform.
The most popular advertising platforms are effective because they’re easy to use and, most importantly, highly trafficked. But for a smaller budget, you might consider a lesser-known alternative to these key players.
When choosing a platform, some other things to consider are the availability of keyword terms, where your target audience spends their time, and your advertising budget.
Here a non-exhaustive list of some of the top PPC platforms.
Google Ads (formerly known as AdWords)
How many times a day do you hear the phrase “Let me Google that?” Probably more than you can count … hence why Google Ads is the king of paid advertising.
On average, Google processes over 90,000 search queries every second, giving you plenty of opportunities to target keywords that will get your intended audience to click. The downside is that keywords are highly competitive on this platform, meaning a larger ad spend.
Bing Ads
The perks of using Bing Ads over Google Ads is a slightly lower CPC at the expense of a larger audience, of course.
Facebook Ads
 Facebook Ads blend in with other posts on the platform.
Facebook Ads blend in with other posts on the platform.
Facebook Ads is a popular and effective platform for paid ads (more commonly used as CPM than CPC), mainly due to its specific targeting options. Facebook allows you to target users based on interests, demographics, location, and behaviors.
Also, Facebook allows for native ads, which means ads are introduced and blend into the social feed. Not to mention, you can use Facebook Ads to advertise on Instagram as well.
AdRoll
 Chipotle retargeting me as I search for dessert recipes.
Chipotle retargeting me as I search for dessert recipes.
AdRoll is a retargeting platform that advertises to people who have already visited your website. For instance, say someone read your article on cheese making. You can retarget them on other sites they visit with display ads that advertise your online cooking classes.
While retargeting is possible with Google Ads, the benefit of using AdRoll is that it can display ads on Google and social media sites, which gives you more opportunities to capture clicks or impressions, depending on your goal.
RevContent
RevContent focuses specifically on promoting content through PPC. It has the same impact as a guest post, where your content is displayed on an external site, except it’s in the form of an ad. You still bid on keywords, and your advertisement is displayed next to content relevant to those keywords. With this platform, you’ll reap the benefits of a low CPC and highly engaged traffic.
How does PPC work?
Pay-per-click, PPC, is a paid advertising model that falls under search engine marketing (SEM). With PPC, the advertiser only pays when people interact with their ad through impressions or clicks.
With that explanation out of the way, now let's look at some benefits of PPC ads.
Benefits of PPC
1. PPC ads are cost-effective.
With PPC ad campaigns, you have complete control over how much you’re willing to spend.
Since you only pay when visitors click the link leading to your website or landing page — with a high chance of conversion — you’ll be getting your money’s worth.
2. PPC ads produce fast results.
Although organic ranking is great, it sometimes takes months or even years to get on the first page on SERPs.
If you’re a startup or small business, you likely don’t have the time to wait for the effect of organic, social, or direct traffic to kick in.
That’s where PPC ads come in.
With optimized PPC ads, you can shoot yourself to the top of the SERP within hours of launching your campaign.
3. You can easily control and test PPC ads.
It’s easy to control the keywords you’re targeting, ad placement, or budget with PPC ads. You can also run A/B split tests with different ads to identify the one that produces the highest return on investment. You can then scale the ads that do well until it no longer produces desirable results.
4. PPC ads allow you to target your ideal customers.
With PPC ads, you can skip right past cold audiences to target a warm audience that’s ready to buy your products and services.
You can bid on keywords that solution-aware personas would search for online. Aside from keywords, PPC ads also offer targeting options like past online activity or demographics.
Another excellent use of PPC ads is to create retargeting campaigns targeting visitors who didn’t purchase after landing on your site.
5. Algorithm changes have little effect on PPC ads.
Between the numerous Google algorithm changes and the 200 ranking factors, trying to get free traffic from search engines is a bit unstable compared to PPC advertising.
With PPC ads, you don’t have to worry about algorithm changes but instead focus on how well your campaigns perform.
6. PPC ads help you rank even with low domain ratings.
Keywords have become increasingly competitive. This makes it more difficult for a business with a low domain authority to get into the top rankings on a search engine or in front of its target audience on a social platform.
With PPC advertising, you can quickly rank for keywords your audience is searching, irrespective of your domain ratings.
7. Data from PPC ads can improve your SEO strategy.
You shouldn’t ditch all your search engine optimization (SEO) efforts altogether — your paid advertising should complement your SEO strategy instead of replacing it.
“When people search for your keywords, you know their search intent and can display the most relevant ad to your audience. This means more clicks and a greater chance of conversion.” - Laura Mittelmann, Paid Acquisition at HubSpot
SEO vs. PPC
SEO refers to the process of optimizing your website to rank high and gain free traffic from search engines. On the other hand, you’ll have to pay for clicks with PPC. Although different, businesses see the best results when they align SEO and PPC in their marketing.
PPC vs. CPC
PPC and CPC are not technically the same thing. PPC refers to a style of marketing that includes paying for advertisements. CPC, or cost-per-click, refers to the amount of money you spend on a single click on your ad.
How to Build a PPC Campaign
Now that you understand the benefits of PPC and have your key terms, let’s dive into crafting a quality PPC campaign using Google AdWords or some other platform.
You don’t need to tackle these items step-by-step, but you will need to work through each of them to ensure that you create an effective marketing campaign.
Set Parameters
I know I said that you don’t need to do these things in order, but you should do this step first. Without parameters, you risk your ad being untargeted and ineffective.
You want to put your ad campaigns into the context of your ultimate business goals. Consider how your paid campaigns will contribute to those goals. Then, think about what you want to accomplish with your ads — whether that be visits, sales, brand awareness, or something else — and how much you’re willing to spend to achieve that goal.
Your ads should encompass a few things:
- Who you want to target
- Theme of your campaign
- How you will measure success
- Type of campaign you will run
Create Goals and Goal Metrics
Your campaign goals will give you something to show for your ad spend as long as you determine how you will measure those goals. Your goal metrics should not be confused with your campaign metrics, which we’ll discuss below.
Let’s touch on some common PPC goals and how to measure them.
Brand awareness is how familiar your target audience is with your company. It might be a good idea to look into display ads for this goal so you can supplement your copy with engaging imagery. You can measure brand awareness through social engagement, surveys, and direct traffic.
Lead generation is the direct result of having a relevant and engaging landing page to follow your paid ad. Since you will create a separate landing page for each ad group, you should be able to easily track lead conversions either in the Google Ads interface via a tracking pixel, or through UTM parameters, if you’re using a tool like HubSpot.
Offer promotion is great if you’re running a limited-time offer, product or service discount, or contest. You should create a dedicated sign-up page or a unique discount code so you know which users came from your ad.
Sales can be measured by how much of your product or service is sold based on your paid ads. You should be able to track this through CMS software or with attribution reporting.
Site traffic is a great goal if you have high-quality content throughout your website. If you’re going to spend money getting people to visit your site, you want to have some level of confidence that you can keep them there and eventually convert them into leads.
Choose Your Campaign Type
You don’t only need to know where you’ll advertise but also how. There are many different types of paid advertising campaigns, and the one you choose depends on where you can reach your audience. That isn’t to say that you can’t advertise through various means; you can also try a combination of campaign types as long as you’re consistently testing and revising.
Search Ads are the most common type of PPC and refer to the text ads that show up on search engine results pages.
Display Ads allow you to place ads (usually image-based) on external websites, including social. There are several ways to buy display ads, including Google Display Network (GDN) and other ad networks.
Learn how to integrate Display Ads into your inbound marketing plan.
Social refers to any ads that you see on social media, including Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, and Instagram. You can pay to show up in your target audience’s social feed or somewhere else within their profile, depending on the platform.
Remarketing can use either cookies or a list of contacts that you upload to target people who have previously engaged with your company through some action. That action could be filling out a form, reading a blog, or simply visiting a page on your website.
Google Shopping is most effective for ecommerce sites. Your ad — including image, price, and a short product description — will show on a carousel on a search page based on your target keywords.
Perform Keyword Research
Each ad group you create needs to be assigned a set of keywords to target — that’s how search engines know when and where to display your ad. The general rule of thumb is to select between one to five keywords per ad group, and those keywords should be extremely relevant — your Quality Score depends on it.
Select keywords that are closely aligned with the specific theme of your ad group. If you find keywords you want to target that fall outside of one theme, you should create a separate ad group for them.
It’s important to note that you’re not stuck with the keywords you start with. In fact, you should closely monitor your keyword list throughout your campaign — eliminating those that don’t bring in the types of visitors that you’re looking for and increasing your bids on those that do. Do your best to select the most relevant keywords, but don’t feel pressured to get it 100% right the first time around.
Set Up Google Analytics and Tracking
Google Analytics is free to use, so there’s no reason why you shouldn’t install it on your website. The tool provides insights into how your website is performing, how users interact with your pages, and what content is attractive to visitors. The information gathered from Google Analytics can be used for PPC and beyond.
Best Practices for a Quality PPC Strategy
You didn’t think we’d let you spend your hard-earned money on advertisements without providing some best practices to follow, did you? Of course not. We want to make sure you succeed with your next PPC campaign. So, let’s get into some PPC strategies that will help you maximize your efforts and your budget.
As a note, we’re going to dive specifically into paid search ads (those little guys you see in search engines) here.
PPC Ad Copy
Bidding on targeted keywords will get your ad in front of the right people; good ad copy will get those people to click on your ad. Like your keywords, your ad needs to solve for the intent of the searcher — you need to give the searcher exactly what they’re looking for and make sure that is clear through the words you use.
Search ads are comprised of a headline, a URL, and a short description, and each of these has limited character requirements to follow. To make the most of this space, make sure your ad copy does the following:
- Speak directly to your target persona.
- Include the main keyword that you’re bidding on.
- Provide an actionable CTA so the searcher knows what to do next.
- Make the offer appealing.
- Use language that matches your landing page copy.
- Perform A/B Split tests with your copy.
Landing Page Best Practices
Arguably the most important element of PPC (after your ad copy) is the page that you send leads to after they click on your ad. This page needs to be highly targeted, relevant to your ad, deliver what was promised, and present a seamless experience.
Why? Because the point of your landing page is to convert your new visitor into a lead or customer. Not only that, but a high-converting landing page will improve your Quality Score, leading to better ad placements. There’s nothing that will diminish PPC profits like a poorly crafted landing page.
What should a PPC landing page include to increase conversions? Glad you asked.
- Strong headline that mirrors your search ad
- Clean design and layout
- Responsive form that is easy to use with a stand-out CTA button
- Copy that is very specific and relevant to your target keywords
- Presents the offer that was promised in your ad
- A/B tested
A/B Testing Your PPC Ads
As a marketer, you’ll rarely throw something out to your audience that works without testing it. PPC campaigns are no different. A/B testing is as critical to your paid ad campaign as is every other element. The goal of testing your ad is to increase both your clickthrough rate and your conversion rate.
The good news is that ads comprise just four parts that you’ll need to test: headline, description, landing page, and target keywords. Minor tweaks to just one of these elements can significantly alter your results, so you want to make changes one at a time so you can keep track of where improvements come from.
Since there are many variations that you could test one at a time, it’s a good idea to list out all the potential tests you can run and prioritize them by most significant impact. Finally, you should allow your ads to run long enough to gather the data you need and test them early enough, so you don’t waste budget on a poor-performing ad.
Maximizing Your ROI
At a high level, maximizing ROI on your ad campaigns means considering customer lifetime value and customer acquisition costs, which will help you determine how much is worth spending on a new lead and how much of that spend can come from paid advertising.
To get more granular, we need to talk inputs and outputs, that is 1) lowering your input (cost per lead [CPL]) and 2) increasing your return (revenue).
There are a few factors to keep an eye on that will affect both, so let’s break it down.
Ways to Decrease Inputs
- Determine an ad budget before you get started.
- Create more relevant ads. The more relevant, the lower your CPC.
- Improve your Quality Score. The higher your QS, the less search engines will charge you for clicks.
Ways to Increase Revenue
- Follow landing page best practices to increase conversion rates.
- Go after quality leads by being specific with your ad. The more quality your leads, the more likely they will convert and eventually become customers.
Additional PPC Tips and Tricks
There are a few other things you can do to maximize the ROI of your paid ads, whether it’s time spent, budget, clicks, or conversions.
Audiences
Google allows you to tailor your audience so you save marketing dollars and get in front of the right people. You can upload a customer list so that you don’t waste money on people who have already bought from you.
Google also has options for prospecting audiences. For instance, In-Market Audiences employs user behavior tracking to put you in front of prospects who are in the market for a product or service like yours.
You can also increase your bid for more relevant subgroups within your target audience — a practice called layering audiences. For example, HubSpot may layer on people who are in the market for CRM software and add a 30% bid adjustment because those people may be more likely to convert.
Bid Adjustments
Bid adjustments allow you to increase or decrease your bids based on performance. You can even make these adjustments based on different categories, like device, demographics, language, and more.
For example, if a keyword isn’t performing as well on mobile as on desktop, you can add a negative bid adjustment so that when someone searches your keyword on mobile, you’ll bid X% lower than your normal bid.
Custom Ad Scheduling
You can set up ad scheduling in Google Ads to display your ad only during specific days and times. This can cut down on ad spend and improve relevance for your target audience.
Sitelink Extensions
Sitelink extensions allow you to supplement your ad with additional information. For instance, if you’re running an ad for a seasonal promotion at a local store, you can add a sitelink extension to display your store hours and location. These extensions take up more real estate on SERPs and, therefore, stand out. Not only that, but they play a role in improving your Ad Rank.
Conversion Tracking
Conversion tracking monitors how your landing page is performing via a tracking code that you place on the page where people land after completing your form (usually a “Thank You” page). By enabling this feature, you’ll be better equipped to make adjustments that can improve your conversions.
Keyword Monitoring
Don’t let too much time pass before you check how your keywords are performing. You can place higher bids on the keywords that are creating the best results for your campaign, and “defund” or eliminate others.
Match Types
Match Types in Google Ads allows you to choose how closely related you want your ad group to be associated with a search team. There are four match types: broad, modified broad, phrase, and exact match. Google will display your ad in results according to your selection.
For example, if your keyword phrase is “how to catch geese” and you select “broad match,” then Google will display your ad for queries that include any word in your key phrase in any order, including “geese catch” and “geese catch how.”
Negative Keywords
A negative keyword list tells search engines what you don’t want to rank for, which is equally as important as what you do. You might know some of these upfront, but likely you’ll determine these keywords by what isn’t performing so well within your campaign.
Social Media Ads
Although CPM is more common on social platforms, social media sites do offer PPC that works similarly to search engine ads in that you set a budget and bid on ad placements.
The difference is social media ads can show up directly in your news feed on most platforms, decreasing the effectiveness of ad blockers. Social platforms, like Facebook, let you set targeted demographics and target people based on interests. While paid search is more keyword-focused, paid social broadens into a demographic focus, leading to more ways to target your persona.
Social media has two paid ad functions that are critical to ad success — retargeting and Lookalike Audiences. Retargeting is remarketing to people based on site visits or manually uploaded contact lists. Lookalike Audiences reviews the people on your marketing list and creates an audience that parallels your list, expanding your potential target. Paid social also allows for a wider variety of ad types, like images, videos, text, and more.
PPC Management and Tracking
Paid advertising is not “set it and forget it.” You need to manage and constantly monitor your ads to ensure that you’re reaching optimal results. Management, analysis, and tracking are crucial to a PPC campaign because they provide you with valuable insights and help you create a more effective campaign.
What is PPC management?
PPC management covers a wide range of techniques, including creating and adjusting goals, split testing, introducing new keywords, optimizing conversion paths, and shifting plans to reach goals.
Managing your PPC means looking at your strategy and ad spend. On the one hand, it means iterating on your plan to optimize keyword effectiveness. On the other hand, it means thinking about how to allocate resources to specific keywords and how to adjust those resources to maximize ROI.
A good management strategy also pays attention to providers — like search engines, social platforms, and ad networks — to monitor changes and updates that could affect paid campaigns.
Overall, PPC management is a hefty undertaking, which is why investing in solid PPC management tools could be a great idea.
Use our PPC management tool to monitor all of your paid campaigns.
PPC Tools and Software
With all of the variables that you need to track, PPC management tools should make things easier. You can opt to monitor your ads within the platform, but if you’re looking for additional assistance and organization, a robust, easy-to-read spreadsheet or sophisticated software that gives you insight into your ad performance is vital.
If you plan to go the software route, there are some features that you want to look for: multi-user support, cross-platform management, A/B testing, scheduling, reporting, and ad grading.
Here’s a list of some popular, highly-rated PPC software and resources.
- HubSpot offers a robust template to help you monitor and manage the moving parts of your campaign, making it easy to keep track of your ad groups, keywords, and A/B tests.
- WordStream automates the tedious parts of setting up and managing your PPC campaign.
- NinjaCat lets you combine all of your analytics from multiple platforms into one report so you can track your entire campaign in one location.
- Optmyzr has end-to-end PPC support, from creation to reporting, and it offers a free trial of its software.
- SEMRush can help you manage the most important part of your PPC campaign — keywords. You can find relevant keywords, manage and optimize your keyword lists, and create negative lists.
- Unbounce is a landing page builder you can use to create landing pages for each of your different PPC campaigns.
- Databox helps businesses track the performance of their ads and displays key metrics across a single dashboard. You can also use Databox’s predictive analysis to estimate how well your ads would do in the future.
- Ahrefs is more than just another SEO tool. You can use Ahrefs to check how well your PPC ads are performing. You can also spy on your competitors’ keywords with Ahrefs.
- Microsoft Advertising Editor (formerly Bing Ad Editor) is a management tool for PPC ads you run through Bing. With this tool, you can manage your bids, research keywords, and make changes to your ads.
PPC Metrics to Track
Metrics are everything (but you already knew that). Here are some key metrics to track within your PPC campaign.
Clicks refer to the total number of clicks you receive on an ad. This metric is affected by your keyword selection and the relevance of your ad copy.
Cost per click (CPC) measures the price you pay for each click on your ad.
Clickthrough rate (CTR) is the percentage of ad views that result in clicks. This metric determines how much you pay (CPC). CTR benchmarks vary by industry.
Impressions are the number of times an ad is viewed. Cost per mille (CPM) is determined for every thousand impressions. Impressions are most relevant for brand awareness campaigns.
Ad spend is the amount you are spending on your ads. You can optimize this by improving your Quality Score.
Return on ad spend (ROAS) is the ROI of your ad campaign. This metric calculates the revenue received for every dollar spent on ads.
Conversion rate refers to the percentage of people that complete the call-to-action on your landing page and become a lead or customer.
Cost per conversion refers to the cost to generate a lead. This is calculated as the total cost of an ad divided by the number of conversions.
Quality Score (QS) determines ad positioning, so it’s an important metric to keep an eye on.
By paying close attention to each of these metrics, you can increase the ROI of your paid campaign and spend less for better results.
Go Paid!
Whether you just started your business yesterday or have been around for decades, PPC just might be the boost you need to get an edge on your competition — or at least ahead of them in the SERPs.
Applying the lessons found in this guide about building a PPC campaign and the best practices for a quality PPC strategy would set you well on your way to improving your website’s traffic and conversions.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August, 2019 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.
Source: HubSpot